Bone Marrow Aspiration/Biopsy
Definition
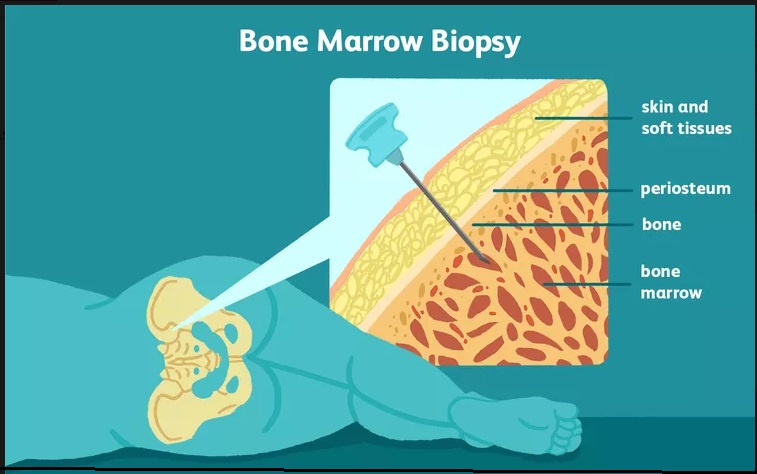
Bone marrow Aspitation = A procedure in which a small sample of bone marrow is removed.
Bone marrow Biopsy = A little of a little more solid portion is collected by a special needle.
Sites of bone marrow aspiration
1. Iliac crest (usually the posterior part
2. Body of the sternum
Bone marrow consists of
A type of stem cells, called pluripotent cells
They are the origin of all blood cells that develop in bone marrow
The process of making the blood cells is called Hematopoiesis
White blood cells, needed to fight infections from bacteria, viruses, and parasites, as well as cancer cells
Red blood cells that carry oxygen to all of the cells in the body
Platelets needed for blood clotting
Stem cells initially divide into two different groups:-
Myeloid cell line:
These cells differentiate into the types of white blood cells (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes), red blood cells, and platelets, which are actually fragments of large cells called megakaryocytes.
Lymphoid cell line:
These cells differentiate into T lymphocytes (T cells) and B lymphocytes (B cells).
Immature white blood cells are called blasts.
Bone marrow also contains connective tissue and the materials that are important to the manufacturing of blood cells, such as iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid.
Bone marrow has a fluid portion and a more solid portion.
In bone marrow aspiration, a needle is used to withdraw a sample of the fluid portion.
In bone marrow biopsy, a special needle is used to withdraw a sample of the solid portion.
Bone marrow aspiration can be performed alone, but it's usually combined with bone marrow biopsy.
Together, these procedures may be called a bone marrow exam.
Indications
Anemia : to find out what type of anemia, such as Aplastic anemia
Blood cell conditions: such as leukopenia, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis, pancytopenia and polycythemia
to find out the Cancers of the blood:- leukemias, lymphomas and multiple myeloma, Acute lymphocytic leukemia, Acute myelogenous leukemia
Cancers that have spread from another area, such as the breast, into the bone marrow (bone metastasis)
Hemochromatosis
Fevers of unknown origin
Purpose
Diagnose a disease or condition involving the bone marrow or blood cells
Determine the stage or progression of a disease
Determine whether iron levels are adequate
Monitor treatment of a disease
Investigate a fever of unknown origin
A bone marrow exam may be used for many conditions. These include:
Risks
Bone marrow exams are generally safe procedures.
Complications : rare
Excessive bleeding, if platelets are low in number
Infection - weakened immune systems
Long-lasting discomfort at the bone marrow exam site
Rarely, penetration of the sternum) during sternal aspirations à heart or lung problems
* * * * * * * * * * * * *
Bone marrow exams are often performed on an outpatient basis.
Sedative may be used
sample (biopsy) are usually collected from the top ridge of the back of a hipbone (posterior iliac crest).
Sometimes, the front of the hip may be used.
Rarely, bone marrow aspiration — but not biopsy — is collected from the breastbone or, in children under the age of 12 to 18 months, from the lower leg bone.
Bone marrow aspiration
The bone marrow aspiration is usually done first. The doctor or nurse makes a small incision in the skin, then inserts a hollow needle through the bone and into the bone marrow.
Using a syringe attached to the needle, a sample of the liquid portion of the bone marrow is withdrawn.
Several samples may be taken.
Check the sample to make sure it's adequate.
Bone marrow biopsy
A larger needle is used to withdraw a sample of solid bone marrow tissue. The biopsy needle is specially designed to collect a core (cylindrical sample) of bone marrow.
After the procedure apply pressure to the area where the needle was inserted to stop the bleeding. Then placed a bandage on the site.
There will be some tenderness for a week or more after your bone marrow exam.
Acetaminophen, paracetamol for relief of pain.
Site care
Wear the bandage and keep it dry for 24 hours. Don't shower, bathe, swim or use a hot tub. After 24 hours you can get the area wet.
Look for the follwoing and report to the doctor
Bleeding that soaks through the bandage or doesn't stop with direct pressure
A persistent fever
Worsening pain or discomfort
Swelling at the procedure site
Increasing redness or drainage at the procedure site
To help minimize bleeding and discomfort, avoid rigorous activity or exercise for a day or two.
Results
The bone marrow samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis.